Cooling tower
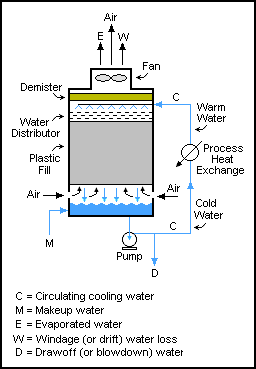
Cooling towers are used to expel heat from warm water coming out of water-cooled condensers in chiller units. The water has absorbed heat from the chiller’s refrigerant as it condenses. There are three ways to transfer heat out of water:
-
Dry cooling: Heat transfer between water and ambient air through a surface for e.g. coils. Closed loop - no water lost. Conduction.
-
Wet cooling: Evaporative cooling. Temperature may go below ambient temperature down to wet-bulb temperature. Open process e.g. pans/pools - water is lost through evaporation.
-
Fluid cooling: Combination of dry and wet cooling. Water is sprayed on a closed loop (e.g coils) containing warm water. Evaporative cooling through the surface. Temperature may go below ambient temperature down to wet-bulb temperature.
In all cases air circulation can be induced using fans or hyperboloid cooling towers (as in power plants) to speed up cooling.
More info: